What is the EDRM?
Understanding the EDRM: An Overview of the Electronic Discovery Reference Model
What exactly is the EDRM?
The Electronic Discovery Reference Model, commonly known as the EDRM, serves as a framework for understanding the process of eDiscovery in legal cases. Developed in 2005 by George Socha and Tom Gelbmann, the EDRM outlines nine stages that form a comprehensive guide to the complex process of managing electronically stored information (ESI). This guide is widely accepted and used by legal professionals, IT specialists, and compliance officers as a standard for eDiscovery protocols and best practices across various industries.
The Nine Stages of the EDRM
The EDRM can be broken down into nine stages, each representing a step in the eDiscovery process.
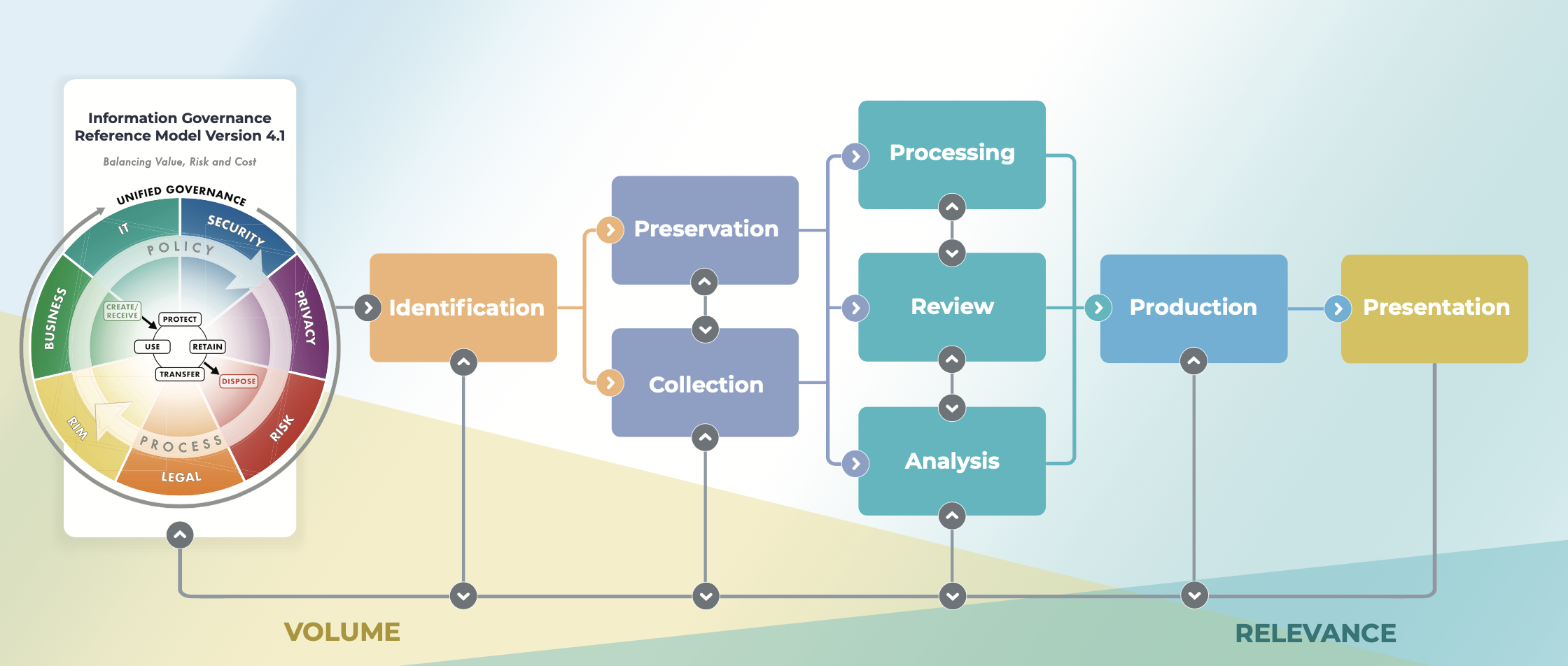
- 1. Information Governance
- At this foundational stage, policies and procedures are established to manage information in a way that mitigates risk and cost in the event of e-discovery. Effective information governance ensures that relevant data can be easily identified and preserved, reducing the workload in subsequent stages. This stage of the EDRM is typically implemented by forward-thinking organizations in anticipation of potential future litigation.
- 2. Identification
- The identification phase involves locating potential sources of ESI and determining its scope, breadth, and depth. Legal teams need to communicate with IT departments and other stakeholders to pinpoint where relevant data resides, be it in emails, databases, social media, cloud storage, or other digital formats.
- 3. Preservation
- Once relevant sources of ESI have been identified, steps must be taken to protect this data from alteration or destruction. Preservation includes implementing legal holds and ensuring that stakeholders are aware of their obligations to keep the information intact.
- 4. Collection
- The collection phase involves gathering ESI for further use in the e-discovery process. The goal is to capture the data in a way that maintains its integrity, ensuring it remains admissible in court. This stage requires careful planning to balance the completeness of the data collection with costs and privacy concerns.
- 5. Processing
- In the processing stage, the sheer volume of collected ESI is reduced and organized. This can involve converting files to a standard format, deleting duplicate files, and extracting text from documents for easier analysis. The aim is to prepare the ESI for review by culling irrelevant data and organizing the remaining information.
- 6. Review
- Review is typically the most time-consuming and expensive part of the EDRM. During this phase, legal professionals examine ESI for relevance to the case, privilege, and issues. Advanced technologies like predictive coding and analytics are often used to accelerate this process.
- 7. Analysis
- Analysis goes hand-in-hand with review, as legal teams evaluate ESI to identify patterns, topics, and behaviors. The goal is to extract meaningful insights that may impact the legal strategy or assist in case settlement discussions.
- 8. Production
- In the production phase, relevant and non-privileged ESI is delivered to opposing counsel and other stakeholders. The production must adhere to agreed-upon formats and protect sensitive or confidential information.
- 9. Presentation
- Lastly, the presentation stage sees the ESI being displayed in depositions, hearings, trials, or other legal proceedings. Data may be presented in various forms such as charts, graphs, reports, or multimedia formats to effectively convey the evidence to the audience.
EDRM Best Practices and Trends
As the volume and complexity of electronic data continue to grow, the EDRM framework needs to evolve to incorporate new best practices and technological advancements. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly crucial in handling the review and analysis phases, offering a faster and more precise examination of massive data sets. Another prevalent trend is the emphasis on privacy and data security, especially with the advent of regulations like the GDPR and CCPA.
Conclusion
The EDRM provides a structured protocol that has greatly facilitated the discipline of eDiscovery. It is the go-to framework for managing digital evidence in legal proceedings. As organizations and legal professionals navigate the ever-expanding digital landscape, understanding and utilizing the EDRM framework effectively guarantees that the discovery process is defensible, efficient, and cost-effective. With a strong grasp of the EDRM, stakeholders can ensure that digital evidence is managed properly from its inception to its ultimate use in legal proceedings.





